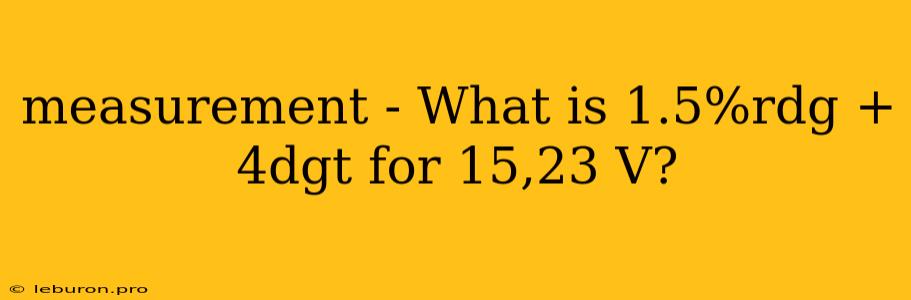Understanding Measurement Uncertainties: Decoding 1.5%rdg + 4dgt for 15.23 V
In the realm of scientific measurement, precision and accuracy are paramount. To properly express the reliability of a measurement, we often employ a combination of measurement uncertainties. One common way to represent this uncertainty is using the formula "1.5%rdg + 4dgt". This formula signifies that the overall uncertainty in a measurement is comprised of two components: a percentage of the reading (rdg) and a fixed digit (dgt) value. Let's delve deeper into the meaning of this formula and illustrate its application using a specific example: a voltage reading of 15.23 V.
Deciphering the Formula: 1.5%rdg + 4dgt
The formula 1.5%rdg + 4dgt encapsulates two distinct types of uncertainties:
1. Percentage of Reading (rdg):
This component reflects the uncertainty inherent in the measurement instrument itself. It indicates that the measurement could be off by a certain percentage of the actual reading. In our case, the 1.5%rdg part signifies that the measurement uncertainty due to the instrument's limitations is 1.5% of the obtained reading.
2. Fixed Digit (dgt):
This component accounts for the resolution or least count of the instrument. It indicates the smallest increment the instrument can display. In our example, 4dgt means that the instrument can only show values to the nearest 4 digits.
Applying the Formula to 15.23 V
To determine the overall uncertainty in a measurement of 15.23 V using the formula "1.5%rdg + 4dgt," we follow these steps:
-
Calculate the percentage of reading uncertainty:
- 1.5% of 15.23 V = (1.5/100) * 15.23 V = 0.228 V
-
Determine the fixed digit uncertainty:
- The instrument's resolution is 4 digits, which means its smallest increment is 0.0001 V.
-
Combine the two uncertainties:
-
The total uncertainty is the sum of the percentage of reading uncertainty and the fixed digit uncertainty.
-
Total uncertainty = 0.228 V + 0.0001 V = 0.2281 V
-
Expressing the Final Measurement with Uncertainty
Therefore, the final measurement with its uncertainty can be expressed as:
15.23 V ± 0.2281 V
This signifies that the actual voltage value lies somewhere between 15.0019 V and 15.4581 V, with a high level of confidence.
Significance of Measurement Uncertainty
Understanding and accurately representing measurement uncertainties is crucial for various reasons:
- Data Analysis: It allows for informed comparisons and analysis of data from different sources.
- Scientific Communication: It facilitates transparent and accurate reporting of experimental results.
- Quality Control: It enables effective monitoring and control of product quality and consistency.
- Engineering Design: It ensures that designs are robust and take into account potential variations in measurements.
Conclusion
The formula "1.5%rdg + 4dgt" provides a clear and concise way to express measurement uncertainties. By understanding its components and applying it to specific examples, we can quantify the reliability of measurements and make informed decisions based on the data. The accurate reporting of uncertainties ensures robust scientific practices and facilitates effective communication within the scientific community. Remember, measurement uncertainties are not just numbers; they reflect the limitations of our measurement instruments and provide crucial insights into the reliability of our results.